Cloud management refers to the exercise of control over public, private or hybrid cloud infrastructure resources and services. A well-designed cloud management strategy can help IT pros control those dynamic and scalable computing environments.
Cloud management can also help organizations achieve three goals:
- Self-servicerefers to the flexibility achieved when IT pros access cloud resources, create new ones, monitor usage and cost, and adjust resource allocations.
- Workflow automationlets operations teams manage cloud instances without human intervention.
- Cloud analysishelps track cloud workloads and user experiences.
Without a competent IT staff in place, it's difficult for any cloud management strategy to succeed. These individuals must possess knowledge of the proper tools and best practices while they keep in mind the cloud management goals of the business.
Why is cloud management important?
Companies are more likely to improve cloud computing performance, reliability, cost containment and environmental sustainability when they adhere to tried-and-true cloud optimization practices.
There are many ways to approach cloud management, and they are ideally implemented in concert. Cost-monitoring tools can help IT shops navigate complex vendor pricing models. Applications run more efficiently when they use performance optimization tools and with architectures designed with proven methodologies. Many of these tools and strategies dovetail with environmentally sustainable architectural strategies to lower energy consumption. Cloud management decisions must ultimately hinge on individual corporate priorities and objectives, as there is no single approach.
Cloud management goals and characteristics
Arguably the biggest challenge to cloud management is cloud sprawl, which is exactly what it sounds like: IT staff loses track of cloud resources, which then multiply unchecked throughout the organization. Cloud sprawl can increase costs and create security and management problems, so IT shops need governance policies and role-based access controls in place.
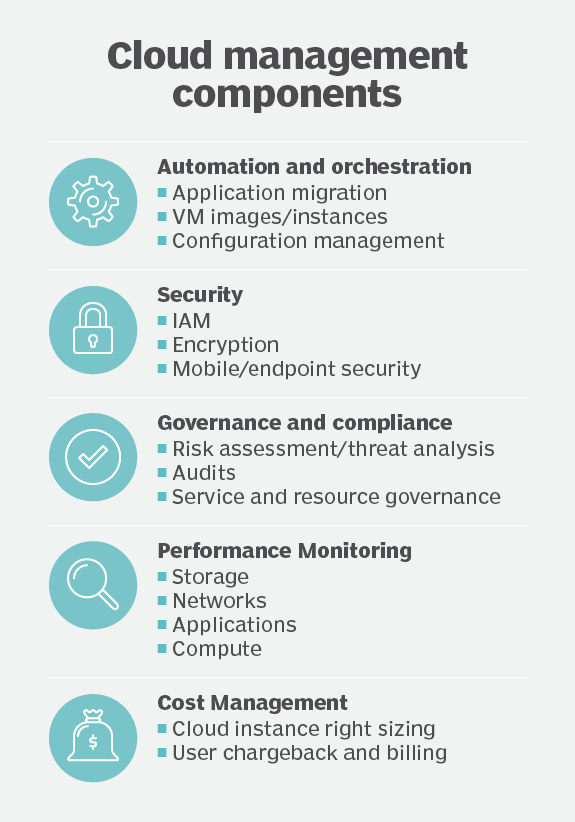
Essential areas of cloud management include the automated and orchestrated instances and configurations, secure access and policy adherence, and monitoring at all levels -- all done as cost-efficiently as possible.
Start with a cloud migration strategy that incorporates proper documentation and ensures only necessary data and workloads are moved off premises. Address multi-cloud management, self-service portals for users and other forms of provisioning and orchestration.
Cloud management platforms provide a common view across all cloud resources to help monitor both internal and external cloud services. Management platform tools can help guide all individuals that touch an application's lifecycle. Regular audits can keep resources in check. Finally, consider third-party tools to help fine-tune enterprise usage, performance, cost and business benefits.
Be sure to set metrics to help identify trends and provide guidance on what you want to measure and track over time. There are plenty of potential data points, but every enterprise should choose the ones that matter most to their business. Consider the following:
- Data about the utilization of a compute instance's volume and performance (processor, memory, disk, etc.) provides insight about the application's overall health.
- Storage consumption refers to storage tied to the compute instances.
- Load-balancing services distribute incoming network traffic.
- Database instances help pool and analyze data.
- Cache instances use memory to hold frequently accessed data and thus avoid the need to use slower media, such as disk storage.
- Functions, also called serverless computing services, are used to provision workloads and avoid the need to supply and pay for compute instances. The cloud provider operates the service that loads, executes and unloads the function when it meets trigger parameters.

